
Herbal Adaptogen Formula
90 Vegetarian Capsules ( SKU: 9280U )
Supplement Facts:
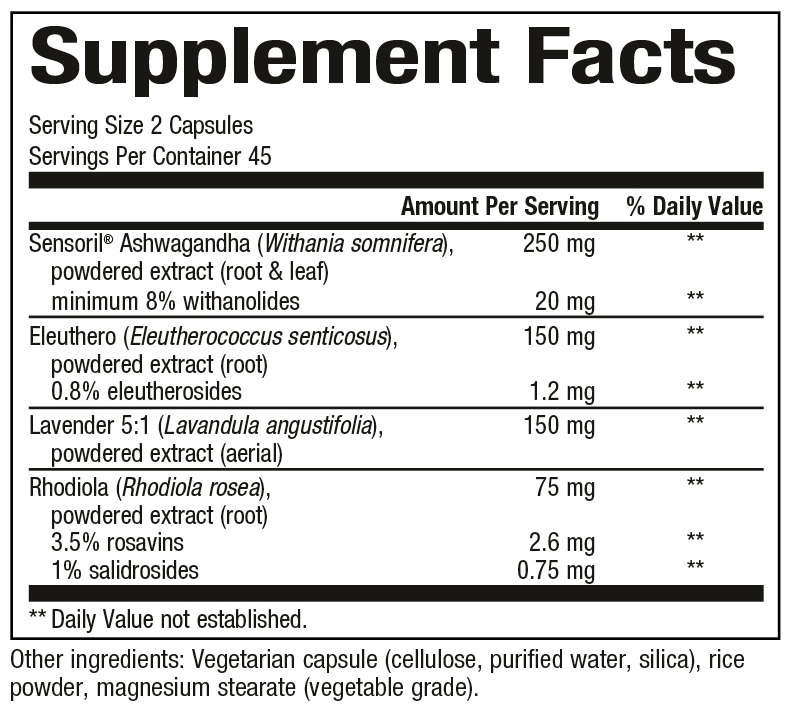
Dosage:
Suggested Usage: 1–2 capsules 2 times per day or as directed by a health care professional.
Warnings:
Consult a health care professional prior to use if you have any type of acute infection or if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Consult a health care professional if symptoms persist or worsen. Consumption with alcohol, other drugs, or natural health products with sedative properties is not recommended. Do not use if you have high blood pressure. Keep out of reach of children.
Allergens:
Contains no artificial colors, preservatives, or sweeteners; no dairy, sugar, wheat, gluten, yeast, soy, egg, fish, shellfish, animal products, salt, tree nuts, or GMOs. Suitable for vegetarians/vegans.
