
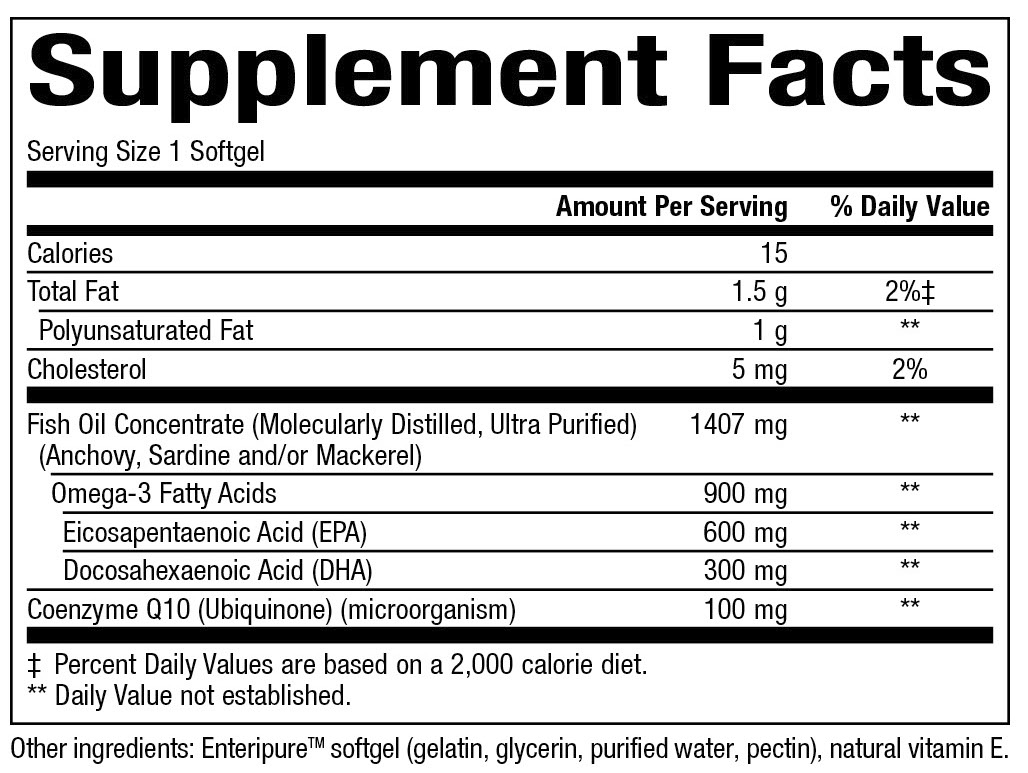
900 mg Omega-3 EPA/DHA • CoQ10 100 mg
900 mg / 100 mg
60 Enteripure® Softgels ( SKU: 9322U )
Supplement Facts:
Dosage:
Suggested Usage: 1 softgel 1–3 times per day or as directed by a health care professional.
Warnings:
Consult your health care professional prior to use if you are pregnant, trying to become pregnant, breastfeeding, taking medication, have a medical condition, or anticipate surgery. Keep out of reach of children.
Allergens:
Contains no artificial colors, preservatives, or sweeteners; no dairy, sugar, wheat, gluten, yeast, soy, corn, egg, shellfish, salt, tree nuts, or GMOs.
