
Optimized Absorption
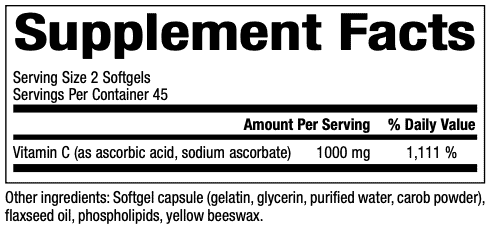
1000 mg per serving
90 Softgels ( SKU: 9412U ), 180 Softgels ( SKU: 9413U )
Supplement Facts:
Dosage:
Suggested Usage: 2 softgels per day or as directed by a health care professional
Warnings:
Consult your health care professional prior to use if you are pregnant, trying to become pregnant, breastfeeding, taking medication, have a medical condition, or anticipate surgery. Keep out of reach of children.
Allergens:
Contains no artificial colors, preservatives, or sweeteners; no dairy, starch, sugar, wheat, gluten, yeast, sesame, egg, fish, shellfish, tree nuts, or GMOs. Sealed for your protection. Do not use if seal is broken. For freshness, store in a cool, dry place.
