
Pharma GABA • Promotes Relaxation
100 mg
90 Vegetarian Capsules ( SKU: 9284U )
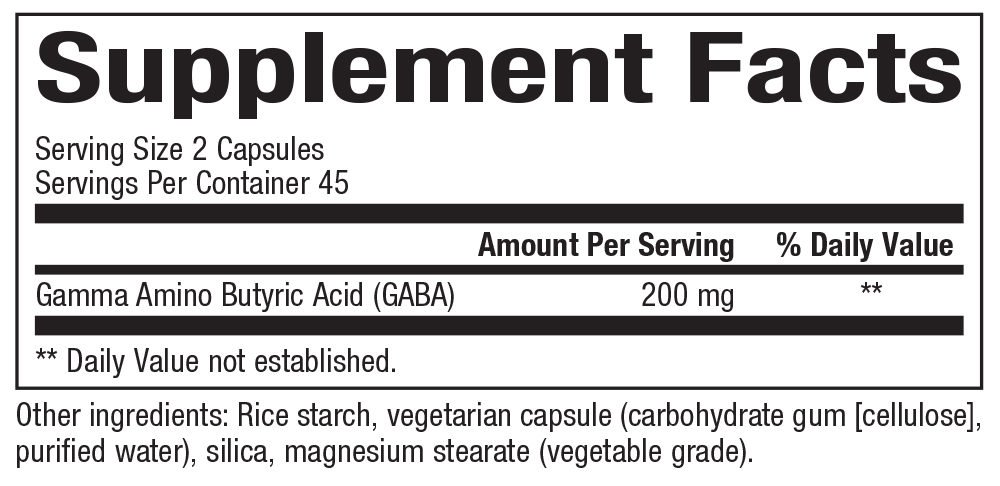
Supplement Facts:
Dosage:
Suggested Usage: 1–2 capsules up to 3 times per day or as directed by a health care professional.
Allergens:
Contains no artificial colors, preservatives, or sweeteners; no dairy, sugar, wheat, gluten, yeast, soy, egg, fish, shellfish, animal products, salt, tree nuts, or GMOs. Suitable for vegetarians/vegans.
